104. 二叉树的最大深度
二叉树节点的深度:该节点到树根的距离,从下到上。
二叉树节点的高度:该节点到叶子节点的最长距离,从上到下。
前序遍历可以求节点的深度,后序遍历可以求节点的高度。
二叉树的最大深度(高度)其实就是根节点的高度,因此可以使用后序遍历。
class Solution {
public int maxDepth(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) return 0;
int lh = maxDepth(root.left);
int rh = maxDepth(root.right);
// 以 root 为根的树的深度是左右子树中最大的深度 + 1
return Integer.max(lh, rh) + 1;
}
}111. 二叉树的最小深度
if (root == null) return 0;
int ld = minDepth(root.left);
int rd = minDepth(root.right);
// 重点,二叉树的深度一定是要触及到叶子节点的
// 如果只有右孩子,则最小深度要从右子树算起
if (root.left == null && root.right != null) {
return 1 + rd;
}
// 如果只有左孩子,则最小深度要从左子树算起
if (root.right == null && root.left != null) {
return 1 + ld;
}
return 1 + Integer.min(ld, rd);222. 完全二叉树的节点个数
遍历树,时间复杂度 O(n)。
// 后序遍历(递归)
class Solution {
public int countNodes(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) return 0;
// 统计左右子树的节点数量,然后再加上根节点的数量
int ls = countNodes(root.left);
int rs = countNodes(root.right);
return ls + rs + 1;
}
}
// 层序遍历(迭代)
class Solution {
public int countNodes(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) return 0;
int count = 0;
Queue<TreeNode> q = new LinkedList<>();
q.offer(root);
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
TreeNode node = q.poll();
count++;
if (node.left != null) {
q.offer(node.left);
}
if (node.right != null) {
q.offer(node.right);
}
}
return count;
}
}题目强调了 “完全二叉树”,可以使用以下解法。
完全二叉树的两种表现形式:满二叉树、普通完全二叉树(即最后一层没铺满)。
可以将完全二叉树看作是一些满二叉树 + 分支节点组成的,如下图:
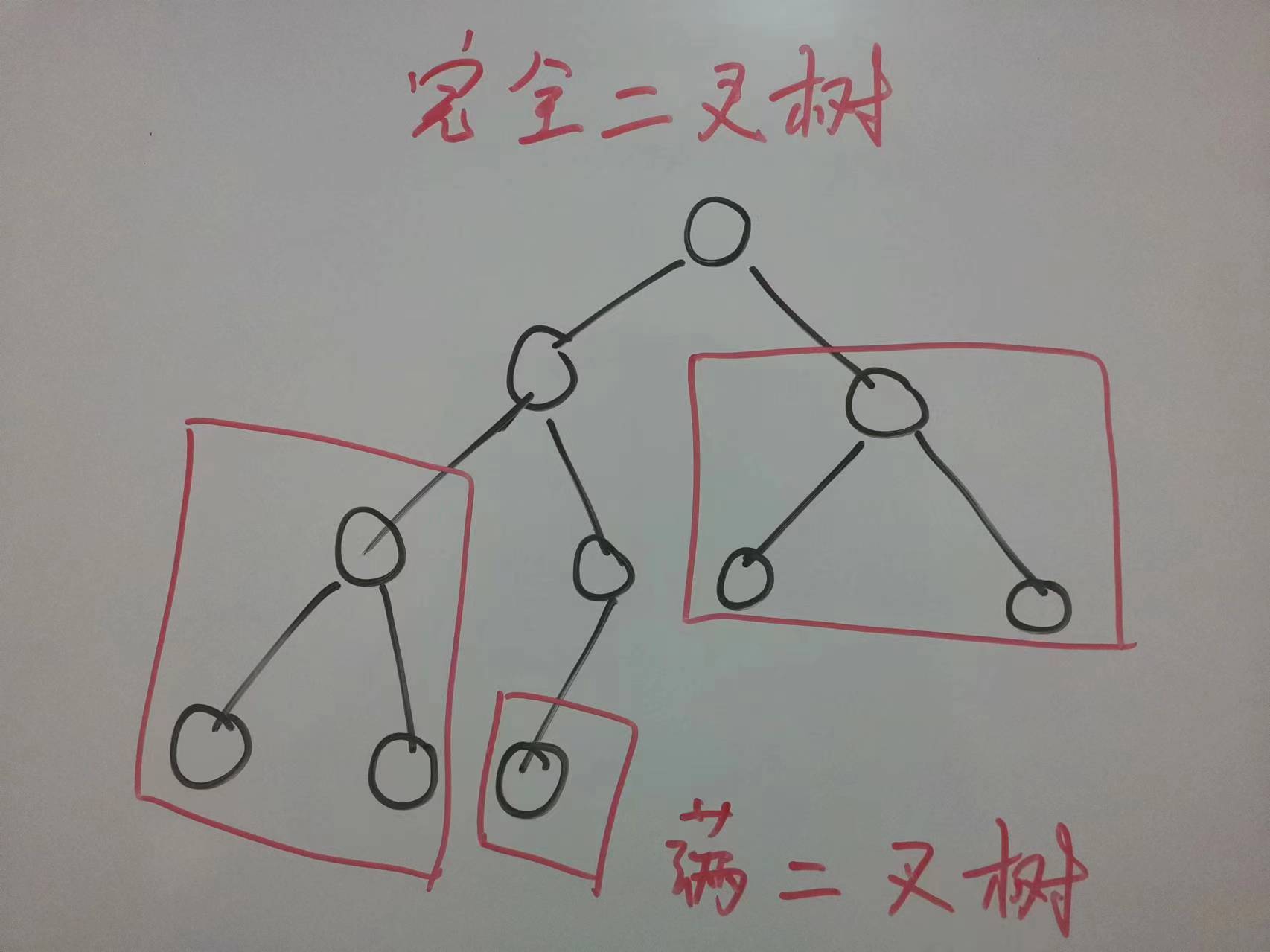
满二叉树的节点数量可以用公式计算:2 ^ 树的高度 - 1。
该题还是可以通过后序遍历的方式计算节点数量,只不过遇到满二叉树时可以通过公式提高计算速度。
if (root == null) return 0;
TreeNode l = root.left;
TreeNode r = root.right;
int ls = 0;
int rs = 0;
while (l != null) {
l = l.left;
ls++;
}
while (r != null) {
r = r.right;
rs++;
}
// 判断是否为 “满二叉树”
// 使用公式计算满二叉树的节点数量
if (ls == rs) {
return (2 << ls) - 1;
}
return countNodes(root.left) + countNodes(root.right) + 1;